fixed prosthesis by anveli dental
Information about fixed prosthesis over implant
The basal implant, anchored in the cortical bone—the strongest part of the jawbone—has been practiced for years. Unlike traditional implants that require osseointegration in spongy bone, basal implants provide immediate stability.
There are two types of dental implants:
The new generation of dental implants (Basal) allows treatment in a single stage with a better success rate.
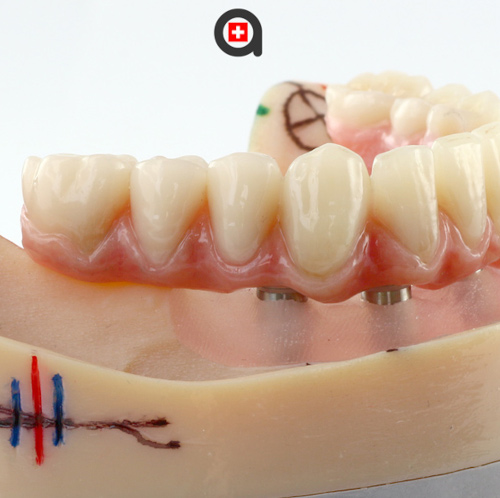
Innovation in dental implantology continues with fixed prostheses that are ever more comfortable and aesthetic.
The latest generation of prostheses uses bi-composite ceramic, a revolutionary material developed by the International Implant Foundation.
What are the advantages?
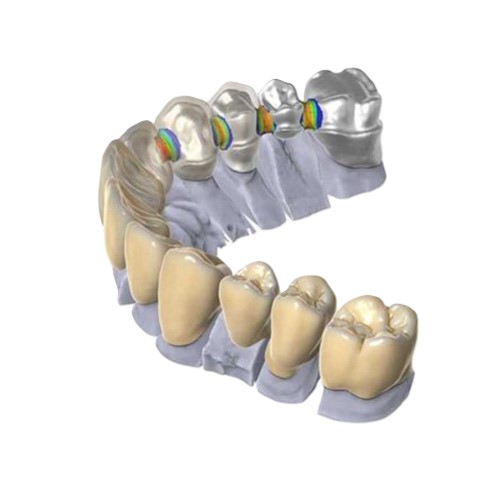
The materials used with the latest generation BAx basal dental implant have continuously evolved since the protocol’s creation over 20 years ago. The most recent innovation from the International Implant Foundation is bi-composite ceramic, a material that combines 75% ceramic and 25% dental composite. This advanced composition offers the best characteristics at this stage of technological development, ensuring durability, comfort, and a natural feel.
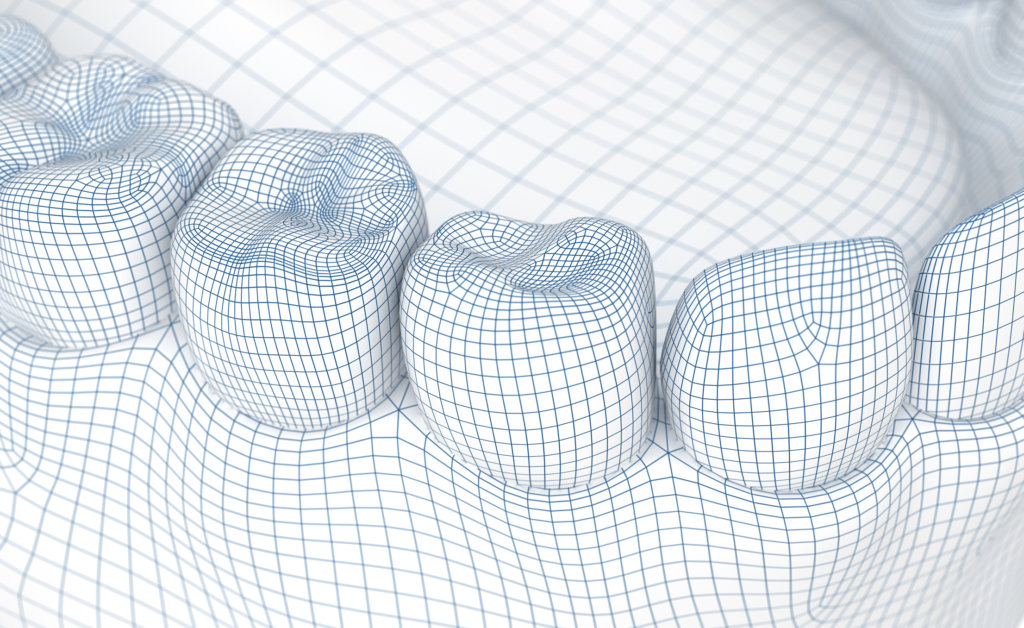
In basal implantology, the prosthesis is loaded immediately, meaning it is securely attached to the basal dental implants within 72 to 96 hours after the procedure. This not only provides comfort for the patient but is also a crucial part of the protocol to ensure proper distribution of chewing forces across all the basal implants. The prosthesis, typically a bridge, acts as a structural connector, linking the implants and enhancing stability.
In basal implantology, your fixed prosthesis (typically a bridge) is attached within 72-96 hours of surgery. This “immediate loading” isn’t just convenient, it’s crucial for:
To ensure precision, our in-house lab conducts 4-5 tests to perfect your prosthesis’ design and fit. This guarantees optimal function and aesthetics.
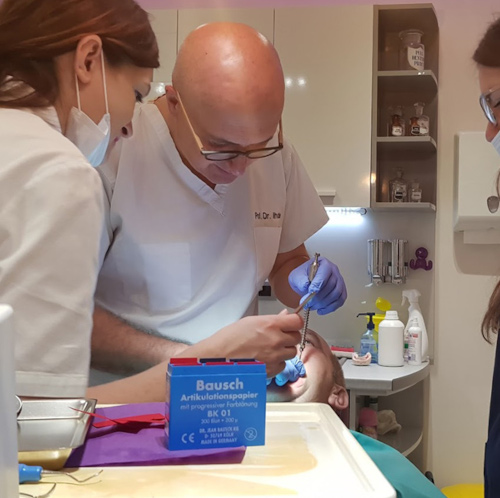
The patient will visit the clinic at least 5 times within 4 days for various tests to achieve the perfect occlusion and design. The final days are dedicated to follow-up visits, ensuring long-term success.
Progress of an operation in basal implantology
To learn more or determine your eligibility for an operation, contact us today.
The fixed dental prosthesis of the basal implant is fixed by cementation. It is an ultra strong ceramic cement. The advantage of cementation is to avoid one of the main causes of the loss of a dental implant traditional: the fracture of the screw connecting the abutment to the dental implant. In most cases, this fracture leads to the replacement of the dental implant.
The fixed dental prosthesis in bi-composite ceramic placed on dental implants of the basal type, allows great comfort since the texture of the crown is closest to a natural tooth. The prosthesis is ultra-light and very thin compared to materials such as ceramic metal which is very heavy and bulky in the mouth.
The dental prosthesis in bi-composite ceramic allows an incomparable aesthetic result. The E-Max ceramic which composes it allows to obtain an incomparable natural result with a transparency of the tooth close to a real tooth.
The oral trial is an Anveli exclusive and an invention of Prof. Ihde and the International Implant Foundation. Before the start of treatment, the patient chooses from a range of sizes, shapes and colors recommended by our prosthetist specializing in facial morphology, it is then possible to choose, for example, teeth that come closest to the original teeth (although it is never possible to reproduce perfectly identical teeth).
The trial in the mouth can only be performed with the new technology of the fixed prosthesis on a bi-composite ceramic basal implant. The day after the operation, the crowns are fixed on the prosthesis in wax of the same color as the future teeth. The patient can thus make modifications on the positioning and the size of his future teeth until obtaining the desired esthetics. This is an important advance in the field of dental prosthetics in comparison with the materials used previously (metal-ceramic or BioHPP), the result of which could only be appreciated at the end of the treatment. Very few modifications could be carried out except for light polishing.
The bi-composite ceramic allows to obtain the best success rates thanks to its lightness and its perfect elastic qualities designed for basal implantology. Although no material presents an infinite resistance, the bi-composite ceramic allows to obtain a very good resistance to masticatory shocks The cortical bone on which the basal dental implant is fixed is much harder and less flexible than the cancellous bone, the goal was to develop a material capable of absorbing chewing shocks while reducing the risk of poor fixation encountered with flexible materials. The success of this material lies in the combination of dental composite and ceramic combining strength and flexibility.
No material is unbreakable, even the most resistant. For this reason, Anveli offers a material that is resistant but also allows repairment even if it is already placed in the mouth of the patient. Bi-composite ceramic is the material closest to the molecular structure which allows in the majority of cases, to repair the prosthesis in the mouth by a simple photopolymerization.
The classic metal-ceramic bridge on basal implants is very widespread among our colleagues. However, in order to guarantee the best success rates and ensure an elasticity that suits the basal implant, its realization required some modifications. Thus, the metal that composes it only represents a thin element that allows the basal implants to be connected to each other. No metal part is in direct contact with the flesh since it is entirely covered with E-Max ceramic (the highest quality of ceramic).
Metal ceramic and zirconia are also possible for fixed prosthesis on dental implants. In some cases, they are recommended for this contact your Anveli Dental advisor and our expertise service who will be able to guide you.
The retraction of the gum is a natural phenomenon which occurs after the extraction of one or more teeth. In order to avoid it, the dental surgeon proceeds to a gingival plasty to reduce the risk of retraction, however, it is always possible for the latter to occur.
With materials such as metallo-ceramic or zirconia, no correction in the mouth is possible. If extractions have taken place, the bridge must then be changed or a space left between the bridge and the gingiva.
The fixed bi-composite ceramic prosthesis can be modified in the mouth and it is therefore possible to add a thin layer of composite to fill any gaps. During the check-up taking place 3 months after the operation.
The design and manufacture of dental prostheses by computer has become for laboratories of dental...
If you’ve lost one or more teeth, your dentist may suggest a fixed dental prosthesis....
Discover the fixed prosthesis on All on 4 or All on 6 implants: definition, advantages,...