La dévitalisation d'une dent (endodontie) est un sujet controversé dans le monde dentaire (si vous ne le saviez pas !). On connaît les risques causés par une mauvaise manipulation lors d'une endodontie trop ou pas assez profonde qui sont de plus en plus rares grâce aux appareils de détection de l'apex. On connaît moins les risques liés aux dents dévitalisées. En effet ce sujet est tabou.: La dévitalisation d’une dent, également appelée endodontie, est un sujet qui suscite de vifs débats dans le domaine dentaire. Si les risques liés à une mauvaise manipulation lors de ce traitement (comme une intervention trop ou pas assez profonde) sont de plus en plus maîtrisés grâce aux appareils de détection de l’apex, les dangers potentiels des dents dévitalisées restent méconnus et souvent passés sous silence.
En effet, ce sujet reste tabou dans le milieu dentaire. Alors que de nombreux dentistes considèrent le traitement du canal radiculaire (ou dévitalisation) comme une procédure sûre et courante, des recherches récentes soulèvent des inquiétudes. Certaines études suggèrent que cette intervention pourrait favoriser le développement de bactéries nocives dans la bouche, voire dans le reste du corps, augmentant potentiellement les risques de maladies cardiovasculaires ou même de cancers. Au sein de notre structure, ce sujet fait l’objet de discussions animées, comme vous pourrez le découvrir dans cet article. Nous explorons les points de vue divergents et les preuves scientifiques pour vous aider à mieux comprendre les enjeux liés aux dents dévitalisées.
Cet article a un rôle purement informatif. Il a pour but de sensibiliser les personnes à risque et d'énumérer les maladies les plus fréquentes. Les maladies citées ci-dessus ne sont en aucun cas une généralité et sont un condensé issu de différents articles médicaux.
Les symptômes énumérés ne doivent pas être source de diagnostic à distance et ne remplacent en aucun cas unevisite chez votre médecin ou votre dentiste.
Qu'est-ce que la dévitalisation d'une dent
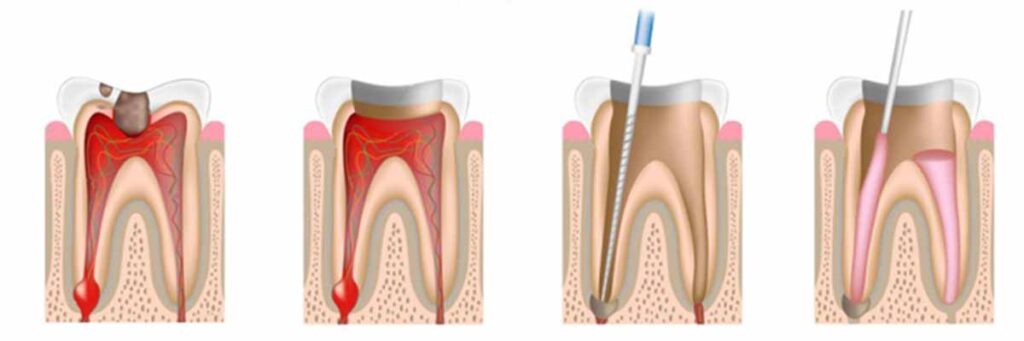
La dévitalisation (endodontie) est un acte de stomatologie réalisé sous anesthésie locale consistant à retirer du canal principal de la dent la pulpe (constituée des nerfs et des vaisseaux principaux). Il est prodigué en 2 étapes.
- Le dentiste, après avoir retiré les tissus de la dent et atteint la pulpe, va retirer cette dernière et nettoyer son canal. Pour cela, une aiguille dont la texture est rugueuse va permettre d’extraire le contenu du canal. Cet acte nécessite une grande précision car la totalité du nerf doit être extrait sans traverser l’apex (l’extrémité de la dent en contact avec l’os). Aujourd’hui des instruments de mesure électriques permettent d’atteindre l’apex de la dent avec une fiabilité d’1/10ème de millimètre. Le canal pulpaire est nettoyé et désinfecté en injectant un produit oxygéné. Le canal va être provisoirement comblé pendant quelques jours afin que les produits antibactériens fassent effet. Un pansement est placé.
- Après quelques jours, le pansement dentaire est retiré et le canal à nouveau nettoyé. Ce dernier est comblé et la dent est reconstituée par un composite de la même couleur que la dent. Jusque dans les années 90, des plombages étaient placés. Aujourd’hui sont utilisés des matériaux photopolymères (plombage blanc sans métal). Le canal pulpaire est nettoyé et désinfecté en injectant un produit oxygéné. Le canal va être provisoirement comblé pendant quelques jours afin que les produits antibactériens fassent effet. Un pansement est placé.
Les plombages peuvent représenter un danger car ils contienne des métaux lourds
Anatomie et structure de la dent
Contrairement à ce qu’elle paraît, une dent n’est pas un tissu inerte. Elle est vivante et constamment irriguée via le canal dentaire d’où passent des nerfs et des vaisseaux sanguins. Cet ensemble forme la pulpe qui traverse la dentine en son centre. La dentine est recouverte par un tissu plus dur, l’émail. La partie de la dent visible se nomme la couronne. La dent est implantée dans le tissu osseux par la racine. Le parodonte entoure la racine de la dent. Il forme le cément qui va lier la dent au tissu osseux. Cette liaison est assurée par des ligaments alvéolaires.
La pulpe et son canal principal présentent de nombreuses bifurcations et ramifications qui irriguent l’ensemble de la dent, un peu comme un arbre possède son tronc et ses branches. Cet ensemble est stérile lorsque la dent est vivante et saine. Lorsque la dent est dévitalisée, elle meurt et dégage des toxines très nocives. C’est toute la question des études sur la toxicité d’un corps mort en bouche.
Le scandale des dents dévitalisées
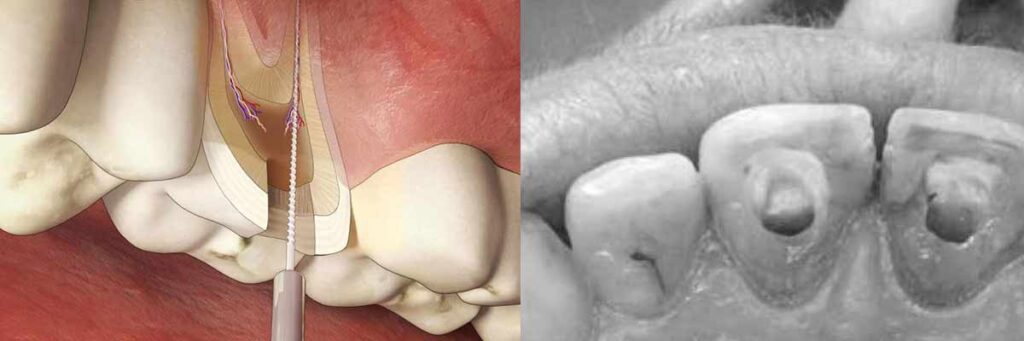
Le scandale des plombages au mercure est bien connu, mais il en existe un bien plus grave selon certains scientifiques. L'empoisonnement causé par les dents dévitalisées. En effet, lors d'une dévitalisation, le canal principal de la dent est nettoyé, cependant la dent est constituée de centaines de sous canaux et bifurcations qui eux ne le sont pas. Ces derniers dégagent des bactéries qui se répandent par absorption vers les tissus osseux puis dans le sang.
Le sujet étant très sensible et peu connu en France par les dentistes eux-mêmes, l'objectif de cet article n'est pas de prendre position pour l'une ou l'autre des thèses mais bien d'informer et partager les avis de différents spécialistes comme c'est le cas dans de nombreux pays.
En France, cet acte est préconisé et remboursé par la sécurité sociale qui elle-même reconnaît les dérives de certains praticiens qui ont recours à cet acte de manière préventive. On retrouve aussi cette dérive dans certaines cliniques pratiquant le tourisme dentaire et qui, afin d'éviter que le patient n'ait à revenir en cas de sensibilité préfèrent traiter directement le canal. Dans le même temps la dévitalisation est déconseillée par l'ordre des stomatologues dans certains pays. On le voit, ce sujet divise une partie de la profession jusqu'aux politiques de santé de certains états.
En France la question est apparue en 2004 dans le rapport remis par Corinne Lepage, alors ex-ministre de la santé qui préconisait l'extraction des dents dévitalisées dans un but thérapeutique. Rapidement contesté par l'ordre des dentistes monté au créneau, ces derniers iront jusqu'en justice pour faire abattre ce texte. L'ancienne ministre qualifiera ce procès de ‘Chasse aux sorcières organisée par un tribu protégeant ses privilèges". Bien que plusieurs études valident la thèse des "anti-dévitalisations", ils perdront leur procès et un chirurgien-dentiste se verra retirer son droit d'exercer.
Alors qu'en penser ? Plusieurs études ont démontré la non-toxicité des produits de comblement utilisés lors de l'endodontie. Mais un problème de méthodologie apparaît dans ces études. L'empoisonnement éventuel proviendrait non pas des produits de complément mais des bactéries se développant dans les sous canaux et bifurcations à la suite de la dégradation des tissus morts. Les études qui elles démontrent que des toxines se dégagent des dents dévitalisées.
Toxicité des dents dévitalisées
Bien que l'on sache aujourd'hui que des bactéries et toxines se dégagent des dents dévitalisées, Il n'est pas simple de prouver que ces dernières sont à elles seules responsables de maladies. On compte cependant de plus en plus d'études le laissant penser. Parmi les plus connues de ces études on retrouve :
- Le cancérologue allemand, le Dr. Joseph Issels insiste pour faire automatiquement extraire toutes les dents dévitalisées, convaincu qu’elles sont à l'origine de nombreuses maladies comme le cancer.
- Le Dr. Price, un dentiste qui s’est fait connaître par des expériences qui consistaient à extraire les dents dévitalisées de personnes malades du cœur ou souffrant d’arthrite puis de les transplanter sous la peau de lapins. Ces derniers développent les mêmes maladies en quelques semaines.
- Le Dr Boyd Haley , professeur et chercheur à l'Université du Kentucky, dénonce un empoisonnement à grande échelle arrangeant les dentistes et l’industrie pharmaceutique. Il a effectué des recherches complémentaires sur les travaux du Dr. M. Price en analysant les bactéries présentes dans les dents dévitalisées. Ses conclusions furent fracassantes : “Environ 25% contenaient des bactéries produisant des toxines plutôt bénignes. 50% des dents étudiées contenaient dans leur structure des bactéries susceptibles de nuire au bon fonctionnement du système immunitaire. Les derniers 25% des dents contenaient des bactéries produisant des toxines plus puissantes que le botulinum (remarque importante, le botulinum est largement reconnu comme la substance la plus toxique pour l'homme). 25% des dents dévitalisées contiennent une toxine plus forte que la plus forte des toxines connues de l'homme. Il avait précédemment été à l'origine du scandale sur les plombages au mercure.
- ou le Prof. Haley recommandent de retirer les dents dévitalisées, même si elles ont l'air sain.
- Les centres Anveli et le Prof. Ihde ont constaté via nos études cliniques que l’os sur les segments traités par des dévitalisations était de plus mauvaise qualité que les segments non traités et que le taux de réussite en implantologie était plus faible sur ces zones.
De nombreuses questions restent malgré tout en suspens. Les matériaux injectés sont-ils parfaitement neutres ? Le fait d’avoir un corps mort (la dent dévitalisée) dans l’organisme peut-il affecter la situation buccale et la santé plus généralement ?
Dévitalisation, un acte rentable
Les français présentent deux à trois fois plus de dents dévitalisées que les autres européens. Le remboursement de la sécurité sociale et des mutuelles a largement contribué à l’explosion de cette pratique même lorsqu’elle n’est pas réalisée dans un but thérapeutique.
Comme nous l'avons vu plus haut, la dévitalisation de la dent a été conçue pour éviter l'extraction de la dent lorsque celle-ci présente une carie profonde. On constate malheureusement sur nos patients que la plupart d'entre eux présentent des dents dévitalisées qui l'ont été de manière préventive. Pratiqué le plus souvent lors de la pose de couronne ou de facette il permet d'éviter que la dent ne devienne sensible au chaud et au froid.
L'atrophie osseuse peut atteindre 5 à 6 millimètres la première année (d'où l'avantage de l'implantation immédiate post extraction) puis de 1 à 2 mm par an.
Dans nos cours et congrès nous rencontrons un grand nombre de dentistes, stomatologues qui ne sont tout simplement pas informés de la toxicité de cet acte. Il est un acte rapide, indolore, rentable puisque remboursé par la sécurité sociale le patient n'est souvent pas contre.
Maladies liées aux dents dévitalisées
De nombreuses bactéries sont présentes dans les dents dévitalisées. Ces bactéries peuvent être la source de maladies ou d'effets néfastes sur la santé. En voici une liste non-exhaustive :
- Les bactéries Fusobacterium, Porphyromonas et Treponema sont liées à l'athérosclérose.
- La bactérie Porphyromonas est liée à la maladie d'Alzheimer par sa capacité à créer une inflammation dans le corps.
- Porphyromonas, Treponema et Tannerella sont liés au contrôle insuffisant de la glycémie et au diabète.
Conclusion
Pourquoi dévitaliser ?
Vous allez penser après avoir lu cet article que nous sommes farouchement contre la dévitalisation. Eh bien non, c'est là le paradoxe. Il n'existe parfois pas d'autres moyens de sauver la dent atteinte. Elle doit être pratiquée cependant de manière parfaitement contrôlée et après avoir tenté de conserver la dent vivante au maximum.
La dévitalisation ne doit pas être réalisée dans le cas de la pose d'une couronne si la dent n'est pas attaquée par une carie ayant atteint le nerf. Lorsqu'il s'agit d'une seule dent le risque est moindre, mais plus le nombre de dents dévitalisées en bouche est important plus le risque d'empoisonnement est élevé.
Comment éviter de dévitaliser une dent?
La première chose à faire est préventive. En conservant une bonne hygiène dentaire pour éviter à toute carie de s'installer. Si le nerf est atteint par la carie alors la question se posera à savoir s'il faut dévitaliser la dent et la conserver avec les risques cités plus haut ou extraire cette dernière et réaliser un bridge (pont), un implant dentaire ou rester édenté. Ce qui rend ce choix encore plus difficile provient du fait qu'il est souvent réalisé sans même que le patient ait donné son accord préalable. Vous vous rendez chez votre dentiste pour vous poser une couronne dentaire ou soigner un mal de dent et ressortez avec une dent dévitalisée.
Que faire si votre dentiste vous dit de devitalize vos dents?
Si votre dentiste vous informe de la nécessité de dévitaliser une dent c'est déjà une bonne chose puisqu'il vous informe avant de pratiquer l'acte. Votre décision dépendra également de la confiance que vous portez en votre dentiste. Demandez-lui avant toute chose s'il estime possible de conserver la dent vivante. Si le nerf n'est pas directement touché il pourra combler la carie et vous constaterez après 5 à 6 semaines si la dent est toujours sensible. Vous devez lui demander de tout faire pour sauver cette dent. Cela peut prendre plusieurs consultations.
Les Sources utilisées pour la rédaction de cet article
- Association américaine des Endodontistes, “Root Canal de la Sécurité.”
- MOI Vienne et coll., “L'effet de canal procédures d'endotoxines et d'endodontie agents pathogènes, par voie Orale de la Microbiologie et de l'Immunologie vol. 22, numéro 6 (décembre 2007).
- PNR Nair, “Sur les causes de la persistance de parodontite apicale,” International Endodontique Journal vol. 39, numéro 4 (avril 2006).
- A. Cope et coll., “Systémique des antibiotiques pour le traitement symptomatique parodontite apicale aiguë abcès apical chez les adultes,” Revues Cochrane, juin 2014.
- Analia Veitz-Keenan et Angela M De Bartolo, “l'Insuffisance de la preuve de l'effet des antibiotiques systémiques sur les adultes avec des symptômes de la parodontite apicale aiguë abcès apical,” evidence-Based Dentistry vol. 15 (2014).
- EL Souza et coll., “De cellules macrophages activation aiguë abcès apical contenu déterminé par l'interleukine-1 Bêta et le facteur de nécrose tumorale alpha de production”, Journal de l'Endodontie vol. 40, numéro 1 1 (Nov. 2014).
- José F. Siqueira, Jr et Isabela N. Rôças, “Microbiologie et de Traitement de Apicale Aiguë Abcès,” Microbiologie Clinique Examens, avril 2013.
- V. Vengerfeldt et coll., “Très divers microbiote dans le traitement de racine dans les cas de parodontite apicale (données de séquençage illumina), ” Journal de l'Endodontie vol. 40, numéro 11 (Nov. 2014).
- Byalakere Rudraiah Chandra Shekar et coll., “Extraits de plantes dans les soins de santé buccodentaire – Un examen de la situation actuelle et de ses besoins futurs,” Pharmacognosie Review, vol. 9, numéro 18 (Juillet-Décembre 2015).
- C. Fernandez et coll., “L'Identification de Synergistetes dans les infections endodontiques,” la Pathogenèse Microbienne, vol. 73, Nov. 2014.

