This article has a purely informative and educational role. It aims to sensitize people on the consequences of poor dental hygiene. The diseases mentioned above are by no means a generality and are a summary of various medical articles.
This article should not be a source of remote diagnosis.
There are different types of infections from different causes and different bacteria. In order to calm the pain and treat it as well as possible, it is necessary to know the causes. gives a brief description of the most common infections and the means of treating them or at least slowing their progression.
Gingivitis
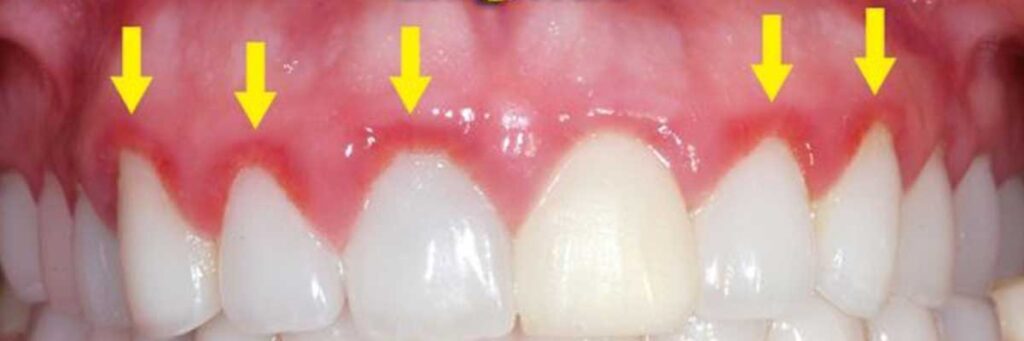
What you should know is that in normal times a tooth does not bleed. If any bleeding appears, the gum is probably affected. Left untreated, the gingivitis will progress to periodontitis.
Symptoms of gingivitis
- Frequent bleeding, especially when brushing teeth
- Bad breath that persists despite brushing teeth
- Excess tartar
Avoid gingivitis
Use dental floss, water jets or interdental brushes for a very thorough cleaning. In case of gingivitis, we recommend Paroflox Surgical mouthwashes to be for 7 days every 3 months. A consultation at the dentist for regular scaling (once a year) is essential!
Periodontitis, gum infection
There are currently several classifications that classify periodontal disease (whether chronic or aggressive onset) but overall, periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissues (periodontium) including the teeth, most often of bacterial origin, which occurs after untreated gingivitis which has progressed to the bone.
As a consequence, the gradual loosening of teeth, bone loss and tooth loss will occur. Immunocompromised people (HIV, cancers) as well as diabetics will be more affected than others by this disease.
Aggressive onset periodontitis usually occurs before the age of 30. Chronic periodontitis is gradual onset, slow but this prolonged infection has adverse effects on the body in general (for example, the risk of cardiovascular problem in diabetics is increased). A periodontal infection poses a risk of infective endocarditis, eye infection and a risk of miscarriage in pregnant women
Treat periodontitis
- Periodontitis at a primary stage: The tooth is not yet loose and does not move, it is still possible to perform periodontal treatment. Many specialists offer this type of care. However, it remains long and the result is not certain. The effects of Paroflox Surgical ® ️ show good results in the primary stage of periodontitis. most effective oral treatment according to our clinical findings.
- Advanced periodontitis: The teeth are loose and moving. In this case, although periodontal treatment is still possible, its success rate is close to 0 if the pocket has reached the apex of the tooth. Curettages will be ineffective. BAx basal implantology will cleanse the mouth, restore functionality and aesthetics in an immediate and lasting way by replacing the affected teeth.
Paroflox Surgical: Against periodontitis
Abscesses and bacterial infections
Periapical abscess forms around the apex of the tooth. It is most often caused by deep decay, a poorly cared for or broken tooth. The nerve will die and bacteria will grow.
The statistics recorded in the Anveli centers show that 72% of apical infections and abscesses come from badly devitalized teeth. The filling material injected too deeply reaches the bone tissues, or conversely not enough, and creates a nerve canal infection.

